Writing blogs on a steam-driven laptop is an extremely slow process, and with extremely poor internet connections it can take me hours, which is the reason I’ve slowed down the number of blogs I do. Technology in Wales seems to be in some sort of reverse decline, and once the black-outs start hitting us it will be even worse. Progress is a funny thing!
Jenny and I enjoyed Patchings Art Festival, where I did two demonstrations in the St Cuthberts marquee to large, enthusiastic audiences. It’s always a joy to work with St Cuthberts Mill, and the Saunders Waterford High-White paper is superb for getting the best out of your watercolours.
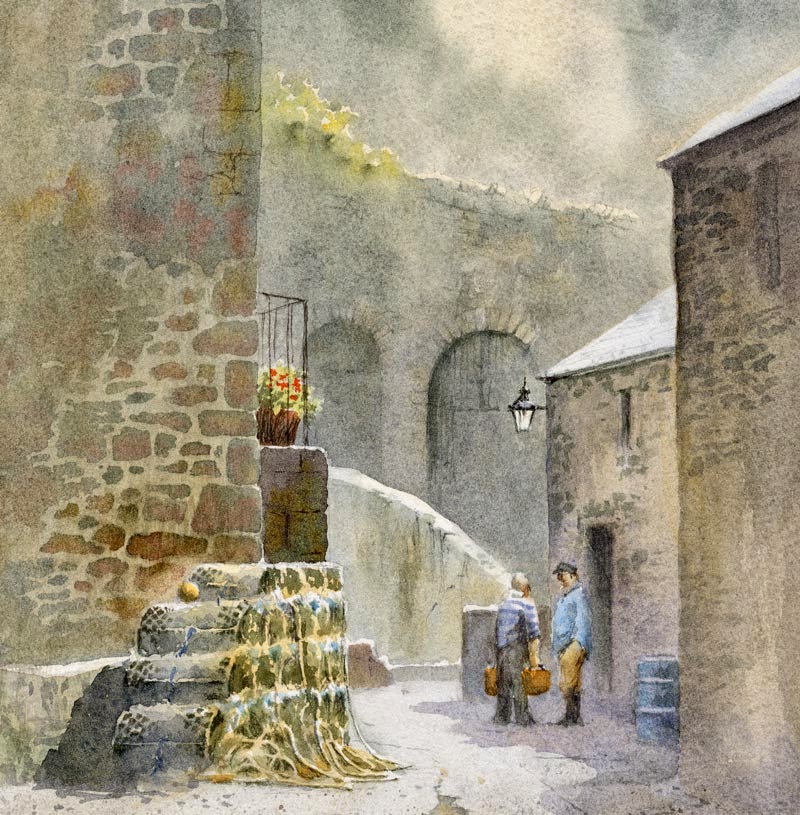
I’ve just taken some new watercolours to Art Matters in White Lion Street in Tenby (Tel. 01834 843375) and this is one, showing a quiet corner of Tenby harbour. The lovely old stone walls provide an interesting backdrop, and these were done by laying an initial wash of Naples yellow over the entire area, and once this was dry painting in the stonework with cobalt blue plus cadmium red, to which I added a few drops of yellow ochre while the stones were still wet. I left some of the Naples yellow showing as light-coloured mortar between the stones. Once again I waited until the whole area had dried and then glazed it all with a weaker wash of cobalt blue and cadmium red. This both imparted a greater sense of unity and slightly softened off the edges of the stonework.
The background has been considerably simplified so that the emphasis is thrown onto the figures in conversation, and the surface was Waterford 140lb NOT, which is excellent for taking repeated washes if necessary.




